Description
Adipocyte differentiation-related protein (ADRP/ADFP) is linked to the membrane
material of globules. Adipophilin (also referred to as PLIN2) has demonstrated the
ability to identify the expression of ADFP in sebocytes and sebaceous lesions.
Sebaceous carcinoma is an infrequent cutaneous malignancy that can resemble other
malignant neoplasms, including basal and squamous cell carcinomas, as well as benign
conditions including chalazions and blepharitis, leading to delayed diagnosis and
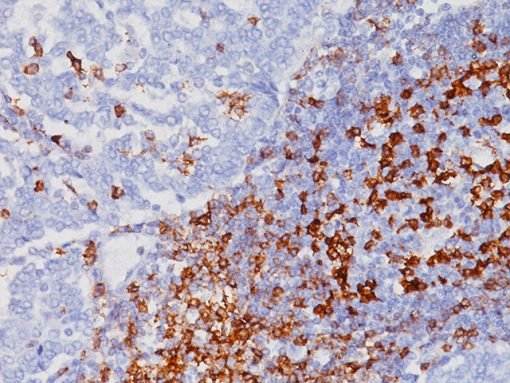
inadequate therapy. Adipophilin was expressed in all 16 (100%) sebaceous adenomas,
exhibiting a distinct pattern of membranous staining with pronounced uptake around
the perimeter of intracytoplasmic lipid vacuoles. Out of 25 sebaceous carcinomas, 23
(92%) exhibited a comparable pattern . Furthermore, in instances of weakly
differentiated sebaceous carcinoma where sebaceous differentiation could not be
accurately assessed in H&E sections, adipophilin effectively highlighted sebocytes and
xanthelasmas . Metastatic renal cell carcinomas exhibited modest to moderate
positivity for adipophilin. Adipophilin may serve as a valuable marker for identifying
intracytoplasmic lipids, particularly in sebaceous lesions. It is particularly beneficial for
recognizing intracytoplasmic lipid vesicles in poorly differentiated sebaceous
carcinomas in difficult scenarios, such as tiny periocular biopsy specimens .
Furthermore, adipophilin has been linked to lipid metabolism in Burkitt lymphoma and
demonstrated pronounced expression in most cases of Burkitt lymphoma . Adipophilin
has been demonstrated to be increased in lung adenocarcinoma, suggesting its
potential as a biomarker for this condition.
Specifications
| Intended Use | RUO |
|---|---|
| Format | Concentrate, Predilute |
| Volume | 0.1 ml, 20 ml, 6.0 ml |
| Source | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Clone | N/A |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Antigen | aa 193-223 |
| Localization | Cell membrane / cytoplasm |
| Positive Control | Skin |