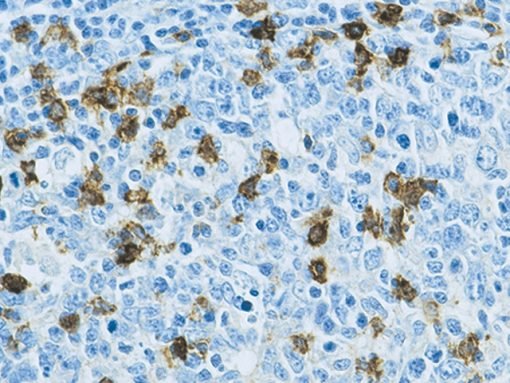
Description
BOB1 (also known as B-cell octamer-binding protein 1) is a protein involved in the regulation of B-cell function and immune responses. The BOB1 primary antibody is used in laboratory testing to detect the presence of BOB1 in cells, particularly in
studies related to B-cells, immune system function, and certain types of cancer. BOB1 is a transcriptional coactivator that interacts with the octamer transcription factor (Oct-1) and is essential for the proper activation of immune-related genes in B-cells. It plays a role in B-cell receptor signaling and the development of B-cells. BOB1 is critical for the proper functioning of B-cells, which are responsible for producing antibodies and responding to infections. The BOB1 primary antibody is esigned to specifically bind to the BOB1 protein in tissue or cell samples. This allows researchers to detect the expression and distribution of BOB1 in various biological contexts using techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, or flow cytometry.