Description
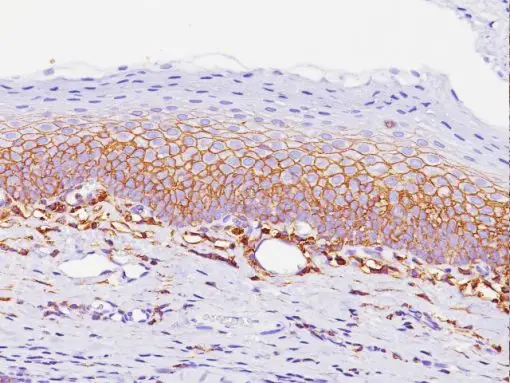
DOG1 (DOG1.1) is a highly valuable monoclonal antibody used for diagnosing gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), particularly c-kit-negative GISTs, as well as differentiating GISTs from other types of tumors. It is also useful in identifying other tissues that expressThe DOG1 antigen is a transmembrane protein expressed on the cell surface. It is encoded by the ANO1 gene (also known as TMEM16A), and it is a calcium-activated chloride channel. DOG1 is considered a highly specific marker for GISTs, which are the most common mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. K9 is a specific monoclonal antibody clone used to detect DOG1. It is widely used in clinical diagnostics, especially in immunohistochemistry (IHC), to identify DOG1 expression in tumor tissue samples. DOG1 is strongly expressed on the surface of GIST cells, particularly in c-kit negative GISTs (those that do not express the typical marker CD117). This makes DOG1 a valuable marker for agnosing GISTs, especially in cases where traditional markers like CD117 may be negative or inconclusive. DOG1 is also expressed in other cell types, including smooth muscle cells, and is found in normal tissues, such as in sweat glands and myoepithelial cells. DOG1 is a calcium-activated chloride channel (TMEM16A) involved in cellular processes such as fluid secretion and ion transport. In the context of GISTs, it is thought to play a role in cell survival, proliferation, and possibly tumorigenesis. TMEM16A, including smooth muscle cells and sweat glands.