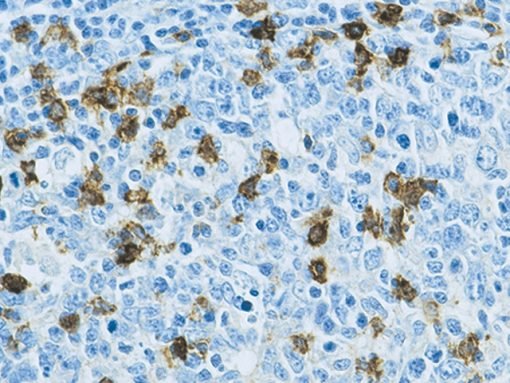
Description
Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor gamma (RORγt) is regarded as a principal regulator in the differentiation of T helper 17 cells (Th17 cells), which play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis. RORγT was first recognized as a transcription factor essential for thymopoiesis by sustaining the survival of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Consequently, RORγt is specifically expressed in the thymus and many immune system tissues, despite the presence of RORγt mRNA in numerous tissues . Regulatory T cells may co-express RORγt and FOXP3, exhibiting both pro-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. Research indicates that a subset of CD8+RORγt+ T cells, characterized by low PD-1 and high OX40 expression, correlates with diminished patient survival, hence suggesting that CD8+RORγt+ T cells are proinflammatory. RORγt appears to be a crucial regulator of immunological homeostasis and proinflammatory responses, and may serve as a potential therapeutic target in inflammatory disorders.
Specifications
| Format | Concentrate, Predilute |
|---|---|
| Volume | 0.1 ml, 0.5 ml, 6.0 ml |
| Intended Use | RUO |
| Localization | Nuclear |
| Clone | 6F3.1 |
| Isotype | IgG2a/kappa |
| Positive Control | Small intestine (Peyer’s patch), tonsil, thymus |
| Source | Mouse Monoclonal |